EP-11 (Myostatin Inhibitor)
$149.95 $109.95
Apo Compounds EP-1 (YK-11 REPLACEMENT) is an Anabolic Phytosteroid (APS), classified as a PGC1-α steroid. It is an anabolic compound, a natural effective muscle builder, an endurance and performance enhancer. It has 42% more myostatin inhibition then the well-known YK-11
YK-11 REPLACEMENT
EP-1 is an Anabolic Phytosteroid (APS), classified as a PGC1-α steroid. It is an anabolic compound, a natural effective muscle builder, an endurance and performance enhancer. It has 42% more myostatin inhibition then the well-known YK-11
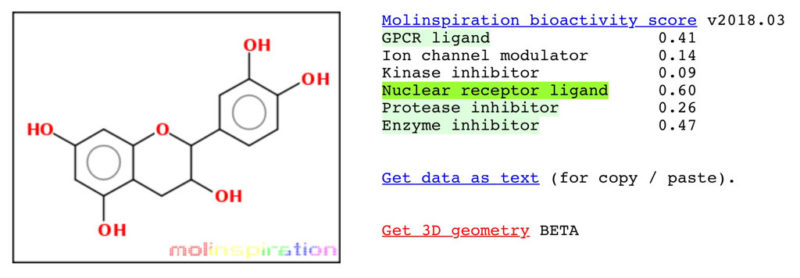
l-Epicatechin is a molecule that is found in chocolate in small amounts, it is a myostatin inhibitor. Myostatin is an enzyme that limits muscle growth. When myostatin is inhibited, deficient, or genetically modified (like in the muscular cattle), it greatly increased muscle mass without the major side-effects associated with AAS.
What EP-1 Does:
Induces muscle regeneration
Improves muscle structure
Improves muscle function
Induces follistatin, a protein that regulates muscle growth
Inhibits myostatin, a protein that stops muscle growth (same mechanism as YK-11)
Promotes mitochondrial biogenesis (muscle energy)
No androgenic activity, so no hormonal side effects
Safe for women
No PCT needed
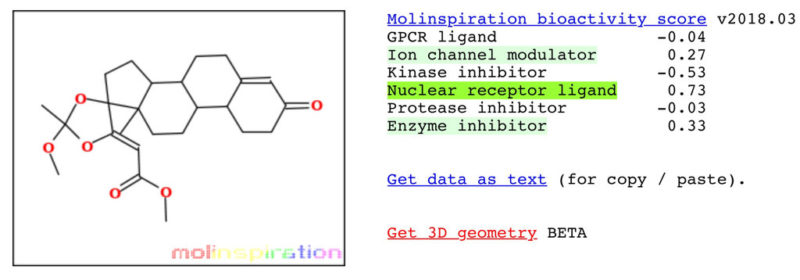
EP-11 has 42% more myostatin inhibition then the YK-11*
Specifications:
100mg/mL | 3.6mL/day | 360mg/day
Serving Size:
1.8mL twice daily | one month supply
Formulation/Ingredients:
EP-1 contains l-epicatechin ((2~{R},3~{R})-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2~{H}-chromene-3,5,7-triol), in a proprietary SMEDDS blend. The active compound is isolated from cocoa.
SMEDDS:
l-epicatechin has medium lipophilicity and requires SMEDDS to be efficient. Our proprietary SMEDDS blend is infused with caprylic acid a natural SARM.
To activate SMEDDS mix the recommended dose by stirring vigorously, shaking, or blending in water, milk, or juice.
Warning: l-epicatechin is a reversible monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B) inhibitor. If you are on any antidepressants (ie. SSRIs, SNRIs, MAOIs) consult with your physician first for possible adverse effects before taking EP-11 [4].
Myostatin Inhibition of EP-11 vs YK-11
EP-1 (l-Epicatechin)
YK-11
* Results according to Molinspiration molecular structure enzyme inhibitor bioactivity.
References
McDonald, C., Henricson, E., Oskarsson, B., Aguilar, C., Nicorici, A., Joyce, N., Reddy, D., Wagner, A., deBie, E., Goude, E., Abresch, R., Villareal, F., Perkins, G., Hathout, Y., Dugar, S. & Schreiner, G. 2015. Epicatechin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis, increases dystrophin and utrophin, increases follistatin while decreasing myostatin, and improves skeletal muscle exercise response in adults with Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD). Neuromuscular Disorders. DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2015.06.456
Gutierrez-Salmeana, G., Ciaraldi, T. P., Nogueira, L., Barboza, J., Taub, P. R., Hogan, M. C., Henry, R. R., Meaney, E., Villarreal, F., Ceballos, G. & Ramirez-Sancheza, I. 2014. Effects of (−)-epicatechin on molecular modulators of skeletal muscle growth and differentiation. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 25(1), pp. 91-94. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.09.007
Li, P., Liu, A., Xiong, W., Lin, H., Xiao, W., Huang, J., Zhang, S. & Liu, Z. 2019. Catechins enhance skeletal muscle performance. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1549534
Jäger, A. K. & Saaby, L. 2011. Flavonoids and the CNS. Molecules, 2011(16), pp. 1471-1485. DOI: 10.3390/molecules16021471
| Size |
|---|
Be the first to review “EP-11 (Myostatin Inhibitor)” Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a review.
Related products
Nootropics
Amino Acids
Amino Acids
Body Building
Anti-Stress
Body Building
Body Building
Alternate Therapies












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.