MASS STACK (20-E and EP-11)
$239.90 $229.95
Looking for that ultimate muscle building stack? APO Compounds 20-E (LGD-4033 & RAD-140 replacement) combined with EP-11 Myostatin Inhibitor (YK-11 replacement) increases the anabolic state providing enhanced muscle growth and recovery, with results more promising than the well known LGD-4033 stacked with YK-11
Looking for that ultimate muscle building stack? APO Compounds 20-E (LGD-4033 & RAD-140 replacement) combined with EP-11 Myostatin Inhibitor (YK-11 replacement) increases the anabolic state providing enhanced muscle growth and recovery, with results more promising than the well known LGD-4033 stacked with YK-11
APO Compounds 20-E Benefits:
RAD-140 & LGD-4033 REPLACEMENT
20 – E is the latest technology 100% Legal ‘herbal’ alternative that rapidly builds lean muscle (LGD-4033 replacement).
More Anabolic per MG than well known steroids such as Dianabol and Testosterone Propionate
Builds LEAN MUSCLE Fast!
Ideal for Men and Women!
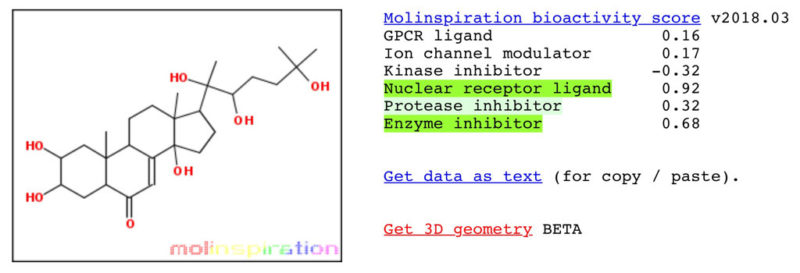
20-E is an Anabolic Phytosteroid (APS), classified as an ecdysteroid. It is an anabolic compound, a natural effective muscle builder, an endurance and performance enhancer. It has 5% more anabolic activity then the traditional AAS Testosterone Propionate*.
Originally 20-hydroxyecdysone was studied and found to combat muscle atrophy and also stopped catabolic expression in cartilage at just 55mg/day HED. In the 1980s it was found to have profound effects surpassing the anabolic activity of many synthetic AAS.
What 20-E Does:
It exhibits a strong hypertrophic effect on muscle fibres [3] Increases protein synthesis [4] Is more hypertrophic then Methandienone (Dianabol), Estradienedione (Trenbolox), and the SARM S-1 [3] [7] The active ingredient is banned by the World Doping Agency in
the Olympics [7] No androgenic activity, so no hormonal side effects [6] Safe for women
No PCT needed
Signals PI3K/Akt pathway, responsible for muscle cell growth and division [3] [5] This is the same pathway IGF-1 uses for its muscle building effect
20-E has 5% more anabolic activity then the AAS Testosterone Propionate*
Specifications:
119mg/mL | 3.6mL/day | 428.4mg/day
Serving Size:
1.8mL twice daily | one month supply
Formulation/Ingredients:
20-E contains 20-hydroxyecdysone ((2b,3b,5b,22r)-2,3,14,20,22,25-hexahydroxycholest-7-en-6-one), in a proprietary SMEDDS blend. The active compound is isolated from Brazilian Ginseng.
SMEDDS:
20-hydroxyecdysone has medium lipophilicity and requires SMEDDS to be efficient. Our proprietary SMEDDS blend is infused with caprylic acid a natural SARM.
To activate SMEDDS mix the recommended dose by stirring vigorously, shaking, or blending in water, milk, or juice.
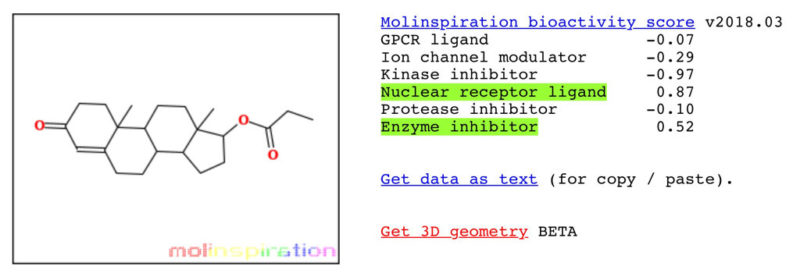
Anabolic Activity of 20-E vs Testosterone Propionate
Testosterone Propionate
* Results according to Molinspiration molecular structure nuclear receptor bioactivity.
References
Hirunsai, M., Yimlamai, T. & Suksamrarn, A. 2016. Effect of 20-Hydroxyecdysone on Proteolytic Regulation in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. International Journal of Experimental and Clinical Pathophysiology and Drug Research, 30(6), pp. 869-877. DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11007
Sheu, S. Y., Ho, S. R., Sun, J. S., Chen, C. Y. & Ke, C. J. 2015. Arthropod steroid hormone (20-Hydroxyecdysone) suppresses IL-1β- induced catabolic gene expression in cartilage. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 15(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-015-0520-z
Parr, M. K., Botre, F., Nab, A., Henjevoss, J., Diel, P. & Wolber, G. 2015. Ecdysteroids: A novel class of anabolic agents? Biology Of Sport, 32(2), pp. 169-173. DOI: 10.5604/20831862.1144420
Gorelick-Feldman, J., MacLean, D., Ilic, N., Poulev, A., Lila, M. A., Cheng, D., & Raskin, I. 2008. Phytoecdysteroids increase protein synthesis in skeletal muscle cells. Journal Of Agriculture And Food Chemistry, 56(10), pp. 3532-3537. DOI: 10.1021/jf073059z
Gorelick-Feldman, J., Cohick, W., & Raskin, I. 2010. Ecdysteroids elicit a rapid Ca 2+ flux leading to Akt activation and increased protein synthesis in skeletal muscle cells. Steroids, 75(10), pp. 632-637. DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2010.03.008
Syrov, V. N. & Kurmukov, A. G. 1976. Anabolic activity of phytoecdysone-ecdysterone isolated from Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iljin. Farmakol Toksikol, 39(6), pp. 690-603. PMID 1030669
Parr, M. 2016. Ecdysteroids As Non-Conventional Anabolic Agents: Pharmacodynamics, Pharmacokinetics, And Detection OfEcdysterone. World Anti-Doping Agency. Freie Universität Berlin, Germany. Online Publication
APO Compounds EP-11 Myostatin Inhibitor Benefits:
YK-11 REPLACEMENT
EP-1 is an Anabolic Phytosteroid (APS), classified as a PGC1-α steroid. It is an anabolic compound, a natural effective muscle builder, an endurance and performance enhancer. It has 42% more myostatin inhibition then the well-known YK-11
l-Epicatechin is a molecule that is found in chocolate in small amounts, it is a myostatin inhibitor. Myostatin is an enzyme that limits muscle growth. When myostatin is inhibited, deficient, or genetically modified (like in the muscular cattle), it greatly increased muscle mass without the major side-effects associated with AAS.
What EP-1 Does:
Induces muscle regeneration
Improves muscle structure
Improves muscle function
Induces follistatin, a protein that regulates muscle growth
Inhibits myostatin, a protein that stops muscle growth (same mechanism as YK-11)
Promotes mitochondrial biogenesis (muscle energy)
No androgenic activity, so no hormonal side effects
Safe for women
No PCT needed
EP-11 has 42% more myostatin inhibition then the YK-11*
Specifications:
100mg/mL | 3.6mL/day | 360mg/day
Serving Size:
1.8mL twice daily | one month supply
Formulation/Ingredients:
EP-1 contains l-epicatechin ((2~{R},3~{R})-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2~{H}-chromene-3,5,7-triol), in a proprietary SMEDDS blend. The active compound is isolated from cocoa.
SMEDDS:
l-epicatechin has medium lipophilicity and requires SMEDDS to be efficient. Our proprietary SMEDDS blend is infused with caprylic acid a natural SARM.
To activate SMEDDS mix the recommended dose by stirring vigorously, shaking, or blending in water, milk, or juice.
Warning: l-epicatechin is a reversible monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B) inhibitor. If you are on any antidepressants (ie. SSRIs, SNRIs, MAOIs) consult with your physician first for possible adverse effects before taking EP-11 [4].
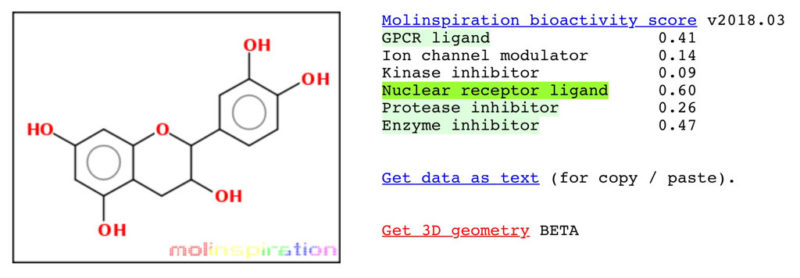
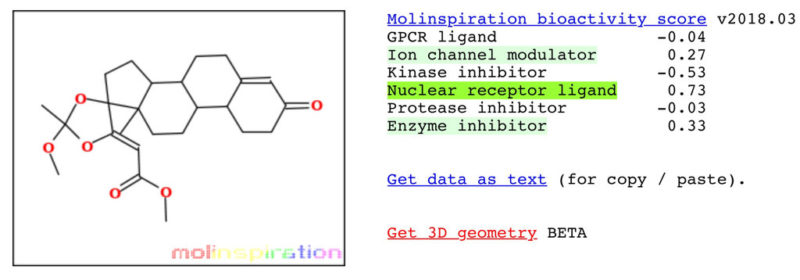
Myostatin Inhibition of EP-11 vs YK-11
EP-1 (l-Epicatechin)
YK-11
* Results according to Molinspiration molecular structure enzyme inhibitor bioactivity.
References
McDonald, C., Henricson, E., Oskarsson, B., Aguilar, C., Nicorici, A., Joyce, N., Reddy, D., Wagner, A., deBie, E., Goude, E., Abresch, R., Villareal, F., Perkins, G., Hathout, Y., Dugar, S. & Schreiner, G. 2015. Epicatechin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis, increases dystrophin and utrophin, increases follistatin while decreasing myostatin, and improves skeletal muscle exercise response in adults with Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD). Neuromuscular Disorders. DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2015.06.456
Gutierrez-Salmeana, G., Ciaraldi, T. P., Nogueira, L., Barboza, J., Taub, P. R., Hogan, M. C., Henry, R. R., Meaney, E., Villarreal, F., Ceballos, G. & Ramirez-Sancheza, I. 2014. Effects of (−)-epicatechin on molecular modulators of skeletal muscle growth and differentiation. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 25(1), pp. 91-94. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.09.007
Li, P., Liu, A., Xiong, W., Lin, H., Xiao, W., Huang, J., Zhang, S. & Liu, Z. 2019. Catechins enhance skeletal muscle performance. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1549534
Jäger, A. K. & Saaby, L. 2011. Flavonoids and the CNS. Molecules, 2011(16), pp. 1471-1485. DOI: 10.3390/molecules16021471
| Size |
|---|
Be the first to review “MASS STACK (20-E and EP-11)” Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a review.
Related products
Body Building
Alternate Therapies
Amino Acids
Fat Burners
Amino Acids
Anabolic Formulas
Nootropics
Body Building












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.